Friday, April 24, 2009
Intel® Core™2 Duo Processors
Now the best gets even better with Intel's latest Core 2 Duo processors built using Intel's 45nm technology, using hafnium-infused circuitry to bring you the latest arsenal of performance-rich technologies. These amazing new processors include up to 6 MB of shared L2 cache, up to 1333 MHz front side bus for desktop, and up to 800 MHz front side bus for laptop.
Intel® Core™ 2 Duo mobile processors
Intel® Core™2 Duo Desktop Processor, Intel® Pentium® Dual-Core Processor and Intel® Pentium® 4 Processor 6x1
Intel Starts Shipping Dual-Core Atom Processor
Intel Core 2 Duo Knocks Down AMD Athlon 64
Intel Core 2 Duo E8400 Dual Core Processor
Intel® Core™2 Extreme processor QX9770
Intel PROSet Network Adapter Driver Set 11.2
Intel Turbo Memory 1.7.0.1029 (8.5.0.1032)
Intel Core 2 Duo Processors
AMD Phenom II X4 940
Ever since the Intel Core processor family has been launched, AMD has been trying hard to keep abreast of the competition.
AMD kept its fingers crossed that the new lineup of Phenom processors would help them grab a larger market share, but the efforts were in vain because of a few glitches in the architecture, and Intel had better performing processors at competitive prices.
This time, AMD is back in action with Phenom II, which is the former Phenom with a couple of tweaks and a leaner design. Now the question is how good Phenom II is and how hard is it going to hit Intel?
Features
Phenom II is built upon the same architecture as that of Phenom, but it’s manufactured using a 45 nm process. Measuring 258 mm2 the die size of Phenom II is 9.5 percent smaller, but yet the transistor count has increased by 68 percent to 758 million.
This increase in the number of transistors has allowed AMD to triple the size of the L3 cache from 2 MB to 6 MB. However, the size of the L1 and L2 cache remains the same. Apart from these, other major improvements are faster L3 cache and more efficient Cool ‘n’ Quiet.While Phenom could only run either at full or half speed, Phenom II can run at four speeds ranging from a minimum of 800 MHz to full speed. In addition to this, AMD has moved away from allowing individual cores to switch independently between different speeds because it caused problems with certain multithreaded applications—runs all its cores at the same frequency, just like the Core i7 except that it cannot completely switch off idle cores.
AMD Launches ATI Radeon HD 4830 for Under $150
"The ATI Radeon HD 4830 graphics card is another example of how AMD's scalable design strategy is paying off," said Rick Bergman, senior vice president and general manager, Graphics Products Group, AMD. "With a single chip we have been able to quickly and efficiently bring to market graphics card designs ranging from below $150 through $549 SEP, with leading performance in every segment. The ATI Radeon HD 4830 continues that great trend, providing tremendous value to gamers for less than $150."
"The $100-$150 graphics card price band represents the ‘sweet spot' of the desktop PC graphics market where the consumer gets the most graphics performance per dollar spent," said Dean McCarron, founder and principal, Mercury Research. "This is where the latest graphics technologies reach the mainstream PC audience, and this is the level that most PC games target."
For gamers looking to get even more performance out of their gaming rigs, ATI Radeon HD 4830 cards support ATI CrossFireX technology allowing gamers to combine as many as four cards in one PC.
AMD maintains that the ATI Radeon HD 4830 offers exceptional HD multimedia performance as well. All ATI Radeon HD 4800 series cards allow users to enjoy HD digital content with uncompromising visual fidelity while helping to enhance the definition and clarity of lower resolution visual media. AMD's second generation Unified Video Decoder (UVD 2.0) ensures users experience smooth HD video playback, and sharp, crisp images and vibrant colors through ATI Avivo HD technology. Combined with capabilities like picture-in-picture, and support for the latest HD audio technologies like 7.1 surround sound, the ATI Radeon HD 4830 graphics card serves up an impressive cinema-quality home entertainment experience.
The ATI Radeon HD 4830 graphics card is supported by a dozen add-in-board companies offering custom designs of the products. Partners include ASUS, Club 3D, Diamond multimedia , Force3D, GECUBE, GIGABYTE, HIS (Hightech Information Systems), Jetway, MSI, Palit Multimedia, PowerColor, SAPPHIRE Technology and VisionTek. It is expected to be available immediately.
Dual Core Atom: Intel D945GCLF2 & Atom 330
The idea of very low power processors that are "fast enough" for many applications is starting to catch on. It would be fair to say that Asus took the world by fire with their original Eee PC, and followed it up with the highly successful Eee PC 901 - spawning a whole new "netbook" category of sub-notebook computers with enough processing power for Internet access and every day tasks. Mind you, Asus dropped the ball by not hitting its initially announced $199 Eee PC price tag, however there are now very capable netbooks around $300, like some models of the Acer AspireOne.
Asus then followed by releasing the Eee Box, bringing low powered tiny desktops to the public - sure they won't run Crysis, but they will do office apps and internet browsing, for less money, and while only sipping power compared to gaming boxes, and they can save even more money by avoiding the Microsoft Tax, by shipping a friendly Linux distribution pre-installed on the computer.
Low power computers are in fact enough for most people's use, and make excellent second, third or fourth computers in a family home. After all, how much power do you need to run Open Office and FireFox? Not much.
Intel Xeon 7460 Six Cores to Bulldoze Opteron Processors
The Xeon 74xx, formerly known as Dunnington, is indeed a very interesting upgrade path for the older quad socket platform. All Xeon 74xx use the same mPGA604 socket as previous Xeons and are electrically compatible with the Xeon 73xx series. The Xeon 73xx , also known as Tigerton, was basically the quad-core version of the Xeon 53xx (Clovertown) that launched at the end 2006. The new hex-core Dunnington combines six of the latest 45nm Xeon Penryn cores on a single die. As you may remember from our dual socket 45nm Xeon 54xx review, the 45nm Penryn core is about 10% to 20% faster than its older 65nm brother (Merom). There is more: an enormous 12MB to 16MB L3 cache ensures that those six cores access high latency main memory a lot less. This huge L3 also reduces the amount of "cache syncing" traffic between the CPUs, an important bottleneck for the current Intel server platforms.
2.66GHz, 6 cores, 3x3MB L2, and 16MB L3 cache: a massive new Intel CPU
With at least 10% to 20% better performance per core, two extra cores per CPU package, and an upgrade that only requires a BIOS update, the newest Xeon 7460 should be an attractive proposal if you are short on processing power.
Six Cores?
Dunnington was announced at the past IDFs as "extending the MP leadership". Readers who read our last quad socket report understand that this is a questionable claim. Since AMD introduced the Opteron 8xxx in April 2003, there has never been a moment that Intel was able to lead the dance in the quad socket server market. Sure, the Intel 73xx was able to outperform the AMD chip in some areas (rendering), but the AMD quad-core was still able to keep up with Intel chip in Java, ERP, and database performance. When it comes to HPC, the AMD chip was clearly in the lead.
Dunnington might not be the darling of Intel marketing, but the chip itself is a very aggressive statement: let us "Bulldoze" AMD out of the quad socket market with a truly gigantic chip that only Intel can produce without losing money. Intel is probably - courtesy of the impressive ultra low leakage 45nm high-K process technology - the only one capable of producing large quantities of CPUs containing 1.9 billion transistors, resulting in an enormous die size of 503 mm2. That is almost twice the size of AMD's upcoming 45nm quad-core CPU Shanghai. Even IBM's flagship POWER6 processor (up to 4.7GHz) is only 341 mm2 and only has 790 million transistors.
Intel Xeon 7460 Six Cores to Bulldoze Opteron Processors,intel,intel xeon, intel xeon 7460, intel 7460, xeon 7460, 7460 six cores to bulldoze, Opteron processors, intel processors,bull doze opteron
Intel Core2 Quad Q9300
When we reviewed the E8500 in March 2008 it had a price of £182 but since then we’ve seen a surprising amount of price compression among the Intel dual cores. The 3.16GHz E8500 has dropped to £123, the 3.0GHz E8400 is £110 and the 2.66GHz E8200 is priced at £106. Who the heck would buy a £106 processor when you can get the next speed bump for only £4 more?
This reduction in price for the Wolfdale dual core Penryns leaves the £150+ price bracket open for affordable Yorkfield quad core processors which is where the Core 2 Quad Q9300 comes into the equation. It has a relatively slow clock speed of 2.50GHz which is achieved by a 7.5x multiplier and a 333MHz/1,333MHz front side bus which is matched by a price of £173. Now that’s cheap for a Yorkfield as faster models shoot past £200 and head for £390 with the Q9550 and upwards to £480 for the aforementioned QX9650.
Things aren’t entirely as they might appear, though, as most Yorkfields have 12MB of L2 cache with 6MB for each core while the Q9300 only has 6MB with 3MB per core. The rest of the features are just as you’d expect from a Penryn which is a significant advance from the 65nm Kentsfield including support for the SSE4.1 instruction set. The move to the 45nm process has allowed Intel to reduce the core voltage from a nominal 1.3V to 1.2V, which in turn reduces the TDP from 105W to 95W.
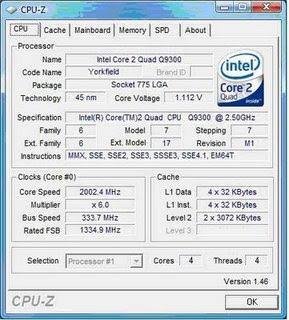 This leads us to wonder how the Q9300 compares with the Core 2 Q6600 which is our absolute favourite processor in the whole of overclockdom. We’ve had our sample of Q6600 for the best part of a year and it’s done sterling service overclocking from its standard speed of 2.4GHz to the dizzy heights of 3.4GHz. Scour the web and the Q6600 crops up time and time again as a champ of a processor and its appeal isn’t hurt one little bit by price cuts that have taken it below £120. Indeed, Intel is taking the fight to the 65nm AMD Phenom by slashing the prices of its own 65nm models and Q6600 is in the thick of that particular battle. Moreover, the Q6600 wipes the floor with Phenom; period.
This leads us to wonder how the Q9300 compares with the Core 2 Q6600 which is our absolute favourite processor in the whole of overclockdom. We’ve had our sample of Q6600 for the best part of a year and it’s done sterling service overclocking from its standard speed of 2.4GHz to the dizzy heights of 3.4GHz. Scour the web and the Q6600 crops up time and time again as a champ of a processor and its appeal isn’t hurt one little bit by price cuts that have taken it below £120. Indeed, Intel is taking the fight to the 65nm AMD Phenom by slashing the prices of its own 65nm models and Q6600 is in the thick of that particular battle. Moreover, the Q6600 wipes the floor with Phenom; period.So, with AMD out of the equation, with the Q9300 we wanted to know how the £117 Q6600 compares to this new £173 chip. For starters, and most obviously, you get an extra 100MHz with Q9300 but that’s certainly not worth an extra £56.
Intel Postpones Launch of New Menlow Atom Chips until Mid-April
Citing un-named "sources at MID makers," the news and rumor site reports Intel has postponed the launch of its Atom Z550 and Z515 Atom CPU s to mid-April, both of which are intended for MIDs. When it launches, the Atom Z550 will run at2.0GHz, making it the fastest clockspeed Atom to date. It will offer the same 2.4W rated TDP, 512KB of L2 cache, and 533MHz frontside bus. The Z515 will run a tick slower at 1.2GHz. Both chips sport an average power consumption of just .22W.
The Z550 will boast support for Intel's US15W chipset, while the Atom Z515 will support both the US15W and low-power UL11L chipsets. In addition, the Z515 will also feature Intel's new Burst Performance Technology (BPT), which will adjust the core clockspeed based on performance requirements.

Intel To Launch Nehalem Server Processor

Intel is expected to introduce Nehalem EP processors and highlight the systems of major computer makers, such as Hewlett-Packard, Dell, and IBM, at its corporate headquarters in Santa Clara, Calif.
Analysts agree that Nehalem EP, with its integrated memory controller for better performance, is poised to deliver more power to meet the increasing demand of virtualization in the data center. In addition, Nehalem-based processors should help with the push toward cloud computing, which typically refers to the running of applications in an Internet server or downloading the software from the Internet each time it's used. Google Apps is an example of business applications delivered via cloud computing. Initially, Nehalem EP processors will primarily be available with four cores. Intel plans to introduce a six-core Nehalem processor and an eight-core design, called Nehalem EX, by the end of the year. But sales of the new Intel products are expected to be slow this year, as companies riding out the economic recession cut IT spending and delay projects. "It's pretty clear that companies are going to be very conservative with the money they spend this year, and that's going to slowdown adoption," John Spooner, analyst for Technology Business Research, told Information Week. Where companies typically replaced old servers every three years, many businesses are likely to stretch out that replacement cycle by an additional year or two, Spooner said. Indeed, worldwide server shipments and revenue fell 11.7% and 15.1%, respectively, in the fourth quarter of last year from the same period a year ago, according to IDC. The downward trend in spending is expected to continue this year. If companies delay purchases of Nehalem EP-based servers this year, then it's unclear how customers will react to the launch next year of Nehalem processors based on Intel's 32-nanometer manufacturing process, which will produce faster, more energy efficient chips than the current batch of 45-nm processors. Companies could skip this year's Nehalem EP systems in favor of those based on the 32-nm variant, code-named Westmere, next year. "In the second half of 2010, when demand for systems in general will return, the combination of Nehalem and Westmere seems more potent on the demand side for really reaping the [performance] benefits," IDC analyst Shane Rau said. However, Intel has options in terms of pricing and adjusting production levels, so Nehalem EP and Westmere could serve different segments of the market.
On the technology side, Nehalem EP's integrated memory controller isn't new to the industry. Intel rival Advanced Micro Devices was the first with an on-chip controller in its 2003 Opteron server processors. While Intel has played down the need for the technology in the past, it's obvious that the demands of computing today have made the need for the higher-performing architecture pivotal.
Other important features within Nehalem are very sophisticated management of multithreading and of the multilevel caches. In addition, the architecture includes more advanced power management technology that computer manufacturers can tap into to reduce a system's energy consumption.
The Nehalem variant, known as Core i7, for high-end desktops and workstations was launched late last year.
Information Week Analytics has published an independent analysis of the challenges around virtualization management
Intel Delays Launch of New Atom CPUs


Just last week we learned that Intel will soon be releasing two new Intel Atom CPU's--the Z550 and the Z515. Now mobile internet device makers have told Digitimes that Intel has postponed the launch of the two new chips until mid-April.
While a delay of just a couple of weeks might not sound like much to consumers, system designers will have to re-juggle their plans to for a new launch date. So far, however, no systems based on the new chips have been announced, as they’re still under wraps at Intel.
Of the two new chips reported to launch soon, one is aimed at the higher-end while the other is for more modest applications. The high-end offering will be the Z550, which will bring the core clock speed to 2.0 GHz. It shall retain the same power characteristics as the 1.86 GHz Z540, thereby giving more performance per watt.
The second new Atom supposedly to be released is the Z515, which is expected to have a TDP of 0.65W to 1.4W, depending on mode, making it a good candidate for MIDs. The chip is to incorporate what is being called Intel Performance Burst Technology, which can put the chip at 800 MHz or 1.2 GHz.
Hopefully the introduction of the new Atom chips will provide a little more variety to the netbook market that’s ruled by the 1.6 GHz model.
Tuesday, April 14, 2009
VoIP Working
How is this useful? VoIP can turn a standard Internet connection into a way to place free phone calls. The practical upshot of this is that by using some of the free VoIP software that is available to make Internet phone calls, you're bypassing the phone company (and its charges) entirely.
VoIP is a revolutionary technology that has the potential to completely rework the world's phone systems. VoIP providers like have already been around for a while and are growing steadily. Major carriers like are already setting up VoIP calling plans in several markets around the United States, and the FCC is looking seriously at the potential ramifications of VoIP service.
Above all else, VoIP is basically a clever "reinvention of the wheel." In this article, we'll explore the principles behind VoIP, its applications and the potential of this emerging technology, which will more than likely one day replace the phone systems
The interesting thing about VoIP is that there is not just one way to place a call. There are three different "flavors" of VoIP service in common use today:
- ATA -- The simplest and most common way is through the use of a device called an ATA (analog telephone adaptor). The ATA allows you to connect a standard phone to your computer or your Internet connection for use with VoIP. The ATA is an analog-to-digital converter. It takes the analog signal from your traditional phone and converts it into digital data for transmission over the Internet. Providers like Vonage and AT&T CallVantage are bundling ATAs free with their service. You simply crack the ATA out of the box, plug the cable from your phone that would normally go in the wall socket into the ATA, and you're ready to make VoIP calls. Some ATAs may ship with additional software that is loaded onto the host computer to configure it; but in any case, it's a very straightforward setup.
- IP Phones -- These specialized phones look just like normal phones with a handset, cradle and buttons. But instead of having the standard RJ-11 phone connectors, IP phones have an RJ-45 enthernet connector. IP phones connect directly to your router and have all the hardware and software necessary right onboard to handle the IP call. wi-fi phones allow subscribing callers to make VoIP calls from any wi-fi hot phones.
- Computer-to-computer -- This is certainly the easiest way to use VoIP. You don't even have to pay for long-distance calls. There are several companies offering free or very low-cost software that you can use for this type of VoIP. All you need is the software, microphone,speakers, asound-card and an Internet connection, preferably a fast one like you would get through a cable orDSL modem. Except for your normal monthly ISP fee, there is usually no charge for computer-to-computer calls, no matter the distance.
If you're interested in trying VoIP, then you should check out some of the free VoIP software available on the Internet. You should be able to download and set it up in about three to five minutes. Get a friend to download the software, too, and you can start tinkering with VoIP to get a feel for how it works.
Using VOIP
Although it will take some time, you can be sure that eventually all of the current circuit-switched networks will be replaced with packet switching network(more on packet switching and circuit switching later). IP telephony just makes sense, in terms of both economics and infrastructure requirements. More and more businesses are installing VoIP systems, and the technology will continue to grow in popularity as it makes its way into our homes. Perhaps the biggest draws to VoIP for the home users that are making the switch are price and flexibility.
 VoIP phone users can make calls from anywhere there's a broadband connection. |
With VoIP, you can make a call from anywhere you have broadband connectivity. Since the IP phones or ATAs broadcast their info over the Internet, they can be administered by the provider anywhere there's a connection. So business travelers can take their phones or ATAs with them on trips and always have access to their home phone. Another alternative is the softphone. A softphone is client software that loads the VoIP service onto your desktop or laptop. The Vonage softphone has an interface on your screen that looks like a traditional telephone. As long as you have a headset/microphone, you can place calls from your laptop anywhere in the broadband-connected world.
Most VoIP companies are offering minute-rate plans structured like cell phones bills for as little as $30 per month. On the higher end, some offer unlimited plans for $79. With the elimination of unregulated charges and the suite of free features that are included with these plans, it can be quite a savings.
Most VoIP companies provide the features that normal phone companies charge extra for when they are added to your service plan. VoIP includes:
- caller ID
- Call waiting
- Call transfer
- Repeat dial
- Return call
- Three-way calling
- Forward the call to a particular number
- Send the call directly to voice mail
- Give the caller a busy signal
- Play a "not-in-service" message
- Send the caller to a funny rejection hotline
Now that we've looked at VoIP in a general sense, let's look more closely at the components that make the system work. To understand how VoIP really works and why it's an improvement over the traditional phone system, it helps to first understand how a traditional phone system works.
Intel to work on 22nm 8-core processor
Intel unveils first Made-in-India chip
Intel Core 2 Duo Processors
Intel Core 2 Duo E8400 Processor BX80570E8400

Intel Core 2 Duo E8400 Processor BX80570E8400Intel® Core™2 Duo processor is the new brand name for our next-generation energy-efficient performance desktop and mobile processors. Formerly known by their codenames Conroe and Merom, the Intel® Core™2 processors for desktop and mobile computers are based on the Intel® Core™ microarchitecture, Intel's new industry-leading foundation for all mobile, desktop and server platforms moving forward.
CES 2007 Best of Innovations HonoreeThe world's best microprocessor, Intel Core 2 Duo microprocessor. Innovations Design and Engineering Awards honor outstanding consumer electronics design and engineering.
Click Banner to view Intel Core 2 Duo Technology flash demo
By offering a single brand name for our mainstream desktop and laptop dual-core processors, Intel's branding strategy makes it simple for consumers and businesses to choose a powerful and energy efficient processor – and makes it easier for developers to "write once, run everywhere."
